| Globally | 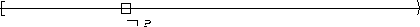 |
| Before R | 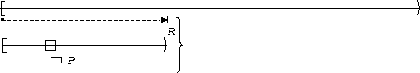 |
| After Q | 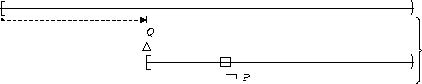 |
| Between Q and R | 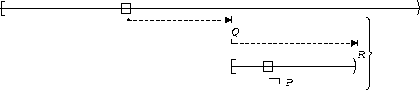 |
| After Q until R | 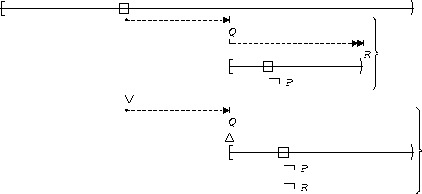 |
This page describe mappings for property patterns in graphical interval logic (GIL). For other information about the patterns click on the pattern links.
Information about the entire pattern system is available at the Specification Patterns Home Page.
P is false :
| Globally | 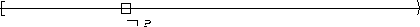 |
| Before R |  |
| After Q |  |
| Between Q and R |  |
| After Q until R |  |
P becomes true :
| Globally | 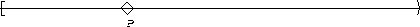 |
| Before R | 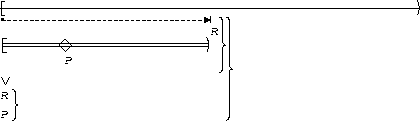 |
| After Q | 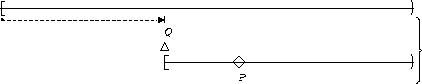 |
| Between Q and R | 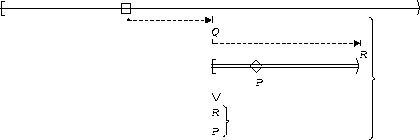 |
| After Q until R | 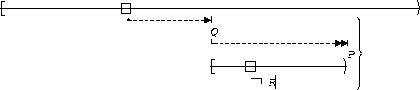 |
In these mappings we illustrate one instance of the bounded existence pattern, where the bound is at most 2 designated states. Other bounds can be specified by variations on this mapping.
Transitions to P-states occur at most 2 times :
| Globally | 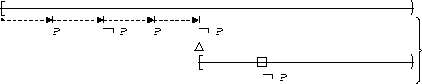 |
| Before R | 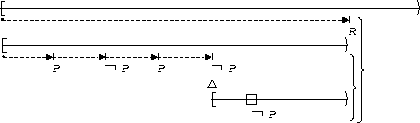 |
| After Q | 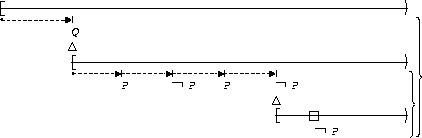 |
| Between Q and R | 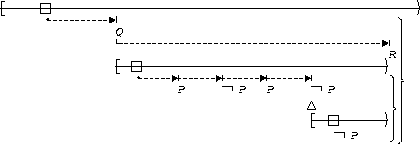 |
| After Q until R | 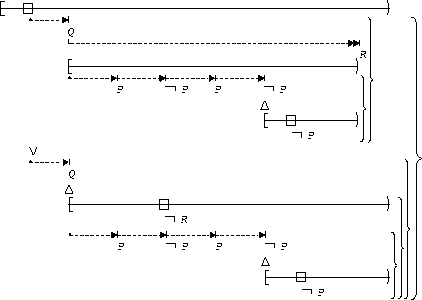 |
P is true :
| Globally | 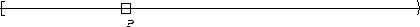 |
| Before R | 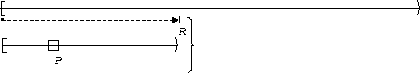 |
| After Q | 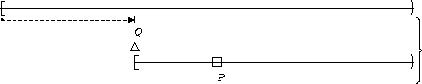 |
| Between Q and R | 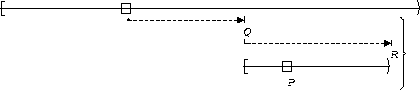 |
| After Q until R | 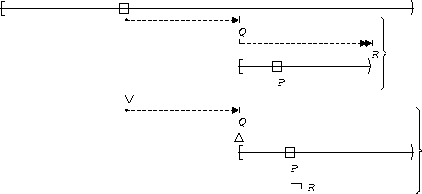 |
S precedes P:
| Globally |  |
| Before R | 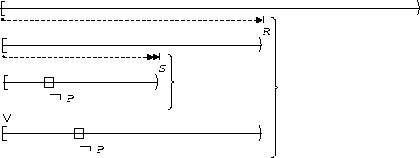 |
| After Q | 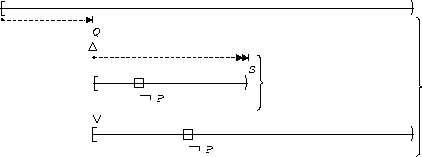 |
| Between Q and R | 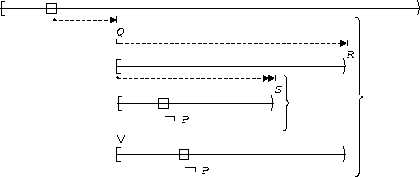 |
| After Q until R | 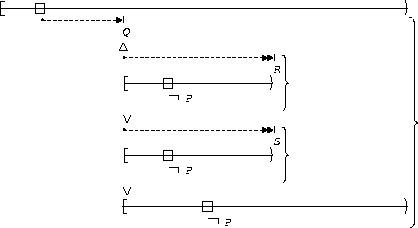 |
S responds to P :
| Globally | 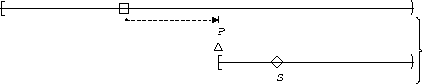 |
| Before R | 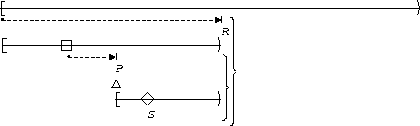 |
| After Q | 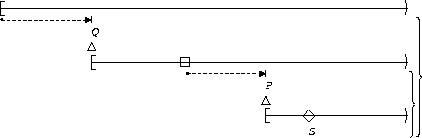 |
| Between Q and R | 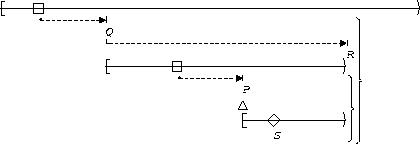 |
| After Q until R | 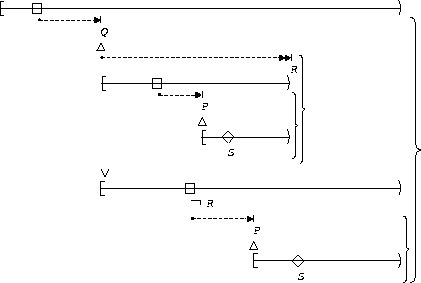 |
This illustrates the 2 cause-1 effect precedence chain.
S, T precedes P:
| Globally | 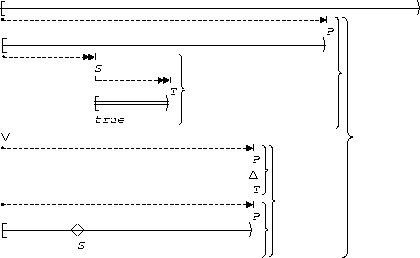 |
| Before R | 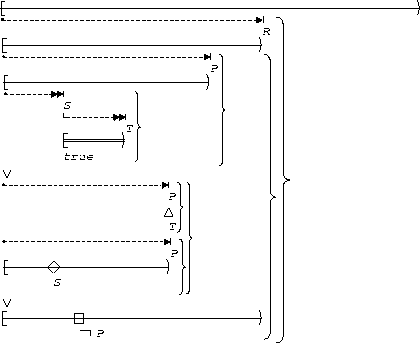 |
| After Q | 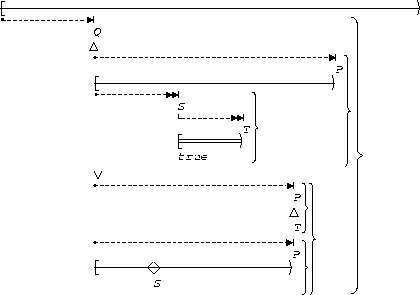 |
| Between Q and R | 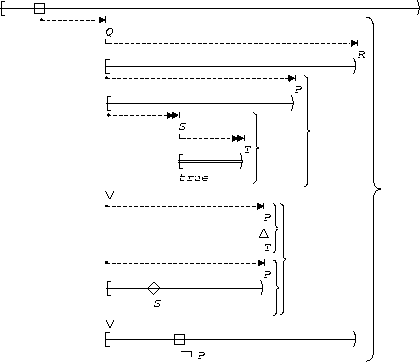 |
| After Q until R | 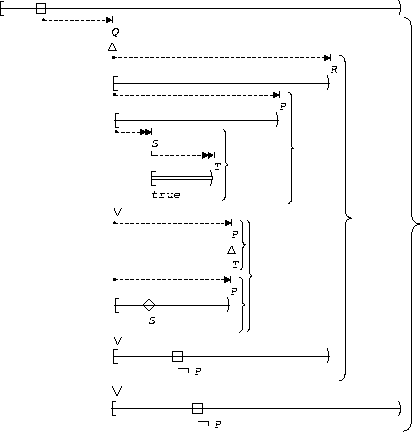 |
This illustrates the 1 cause-2 effect precedence chain.
P precedes (S, T):
| Globally | 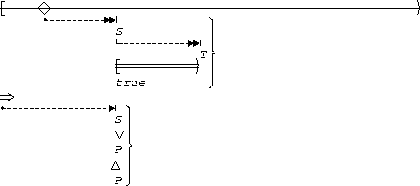 |
| Before R | 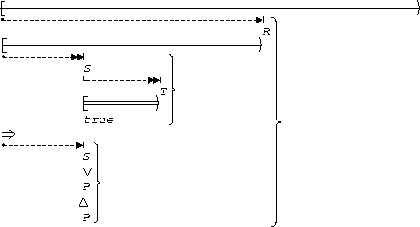 |
| After Q | 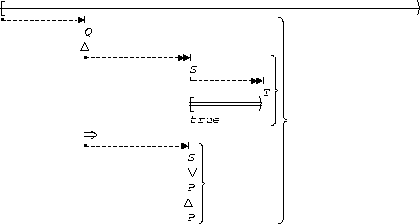 |
| Between Q and R | 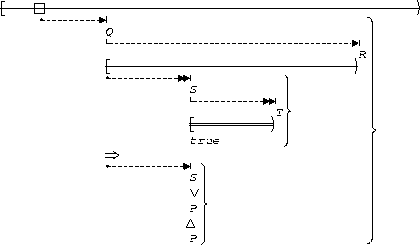 |
| After Q until R | 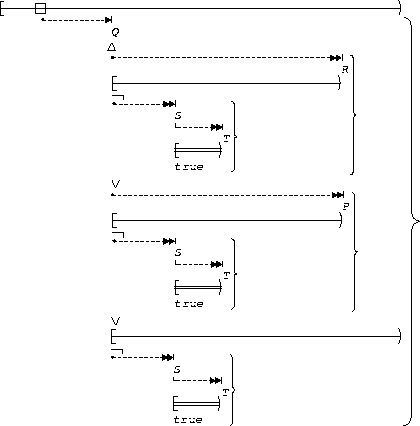 |
This illustrates the 2 stimulus-1 response chain.
P responds to S,T:
| Globally | 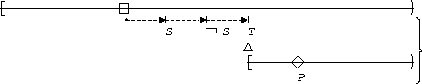 |
| Before R | 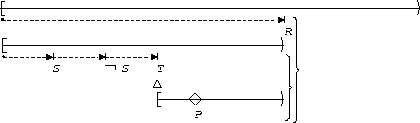 |
| After Q | 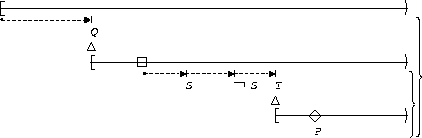 |
| Between Q and R | 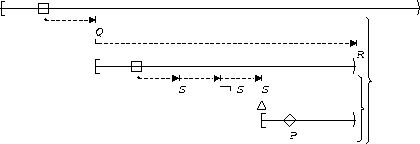 |
| After Q until R | 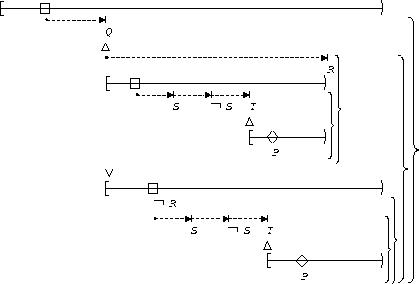 |
This illustrates the 1 stimulus-2 response chain.
S,T responds to P:
| Globally | 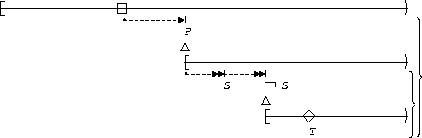 |
| Before R |  |
| After Q | 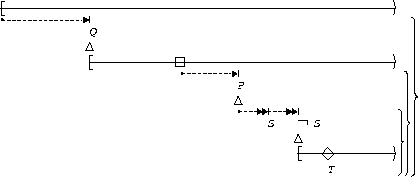 |
| Between Q and R | 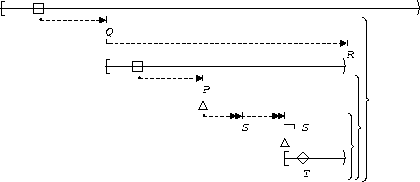 |
| After Q until R | 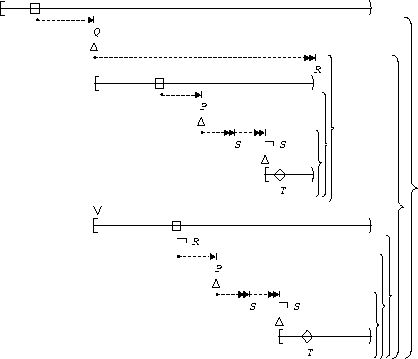 |
Not available yet.